Happiness Hormones
Hey there! Let’s dive into the fascinating world of happiness—it’s a bit like a cocktail of emotions stirred by a bunch of factors. Picture it as a mix of ingredients, some from the inside, and others from the outside. Now, we don’t have a VIP “happiness hormone,” but we do have a squad of neurotransmitters doing the mood regulation dance. They’re the rockstars behind the scenes, and we call them the “happiness hormones.” Drumroll, please: dopamine, serotonin, oxytocin, and endorphins.
Dopamine:

PinterestDopamine is a neurotransmitter, a chemical messenger that plays a crucial role in various functions within the brain and body. It is often referred to as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter because of its association with pleasure, reward, and motivation. In the brain, dopamine is produced in several areas, with the substantia nigra and the ventral tegmental area being primary sources. The synthesis of dopamine involves the conversion of the amino acid tyrosine into L-DOPA, which is then further transformed into dopamine. This process occurs in specialized cells called dopaminergic neurons. Dopamine impacts our happiness by influencing the brain’s reward system. #Happiness Hormones
When we engage in activities that bring pleasure or satisfaction, such as eating, socializing, or accomplishing a goal, dopamine is released in certain brain regions. This release of dopamine reinforces the behavior, creating a sense of reward and encouraging us to repeat those actions. Moreover, dopamine is linked to motivation and goal-directed behavior. It helps drive us to pursue rewards and achieve our objectives, playing a key role in the experience of accomplishment and satisfaction. In situations where dopamine levels are imbalanced, it can contribute to conditions like depression, addiction, or other mental health disorders. #Happiness Hormones
It’s important to note that while dopamine is associated with feelings of happiness, an oversimplified view of its role can lead to misconceptions. The relationship between neurotransmitters and emotions is complex, and various factors contribute to our overall sense of well-being. In summary, dopamine is a neurotransmitter produced in the brain that plays a pivotal role in the experience of pleasure, reward, and motivation. Its impact on our happiness is interconnected with the brain’s reward system, influencing our responses to pleasurable activities and encouraging behaviors that contribute to our well-being. #Happiness Hormones
Serotonin

PinterestSerotonin is a neurotransmitter, a chemical messenger in the brain that plays a crucial role in regulating mood, happiness, and overall well-being. It is often referred to as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter because of its influence on mood and emotions. In terms of production, serotonin is synthesized from the amino acid tryptophan, which is obtained through the foods we eat, such as turkey, chicken, eggs, and dairy products. Once tryptophan is absorbed into the body, it undergoes a series of chemical reactions to ultimately produce serotonin. The impact of serotonin on happiness is multifaceted. It helps regulate mood by contributing to feelings of contentment and satisfaction. #Happiness Hormones
Adequate serotonin levels are associated with a sense of emotional stability and resilience to stress. Low levels of serotonin, on the other hand, have been linked to conditions like depression and anxiety. The intricate relationship between serotonin and happiness involves its interaction with receptors in the brain. Serotonin binds to specific receptors, influencing the transmission of signals between nerve cells. This interaction is believed to modulate mood and emotional responses, helping to create a positive and balanced mental state. Various factors can influence serotonin levels, including genetics, diet, and lifestyle. Exercise, exposure to natural light, and certain activities like socializing can contribute to serotonin production. #Happiness Hormones
Additionally, medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly prescribed to treat conditions like depression by increasing the availability of serotonin in the brain. In summary, serotonin is a neurotransmitter essential for regulating mood and happiness. Its production is influenced by the intake of tryptophan-rich foods, and its impact on mental well-being involves complex interactions with receptors in the brain. Understanding and maintaining optimal serotonin levels through lifestyle choices and, when necessary, medical interventions can contribute to a positive and balanced emotional state. #Happiness Hormones
Oxytocin

Oxytocin hypothetic Image By PinterestOxytocin is a hormone and neuropeptide that plays a crucial role in social bonding, trust, and emotional well-being. Often referred to as the “love hormone” or “bonding hormone,” oxytocin is produced in the hypothalamus, a region of the brain, and is released into the bloodstream by the pituitary gland. The production and release of oxytocin are associated with various social and intimate interactions. For instance, it surges during activities like hugging, kissing, and other forms of physical touch, as well as during childbirth and breastfeeding. In romantic relationships, oxytocin levels tend to rise during moments of closeness and intimacy. The impact of oxytocin on happiness is attributed to its ability to foster feelings of connection, trust, and social bonding.
When oxytocin levels are elevated, individuals may experience increased feelings of warmth, empathy, and generosity. This can contribute to a sense of well-being and happiness, as social connections are fundamental to human fulfillment. Research suggests that oxytocin not only influences social relationships but also has broader effects on mood and stress regulation. It may play a role in reducing stress and promoting a sense of calm, further contributing to an overall positive emotional state. #Happiness Hormones
While oxytocin is associated with positive emotions and social bonding, it’s important to note that its effects are complex and can vary among individuals. Factors such as genetics, environment, and personal experiences all contribute to the intricate interplay of oxytocin in shaping emotional responses. In summary, oxytocin is a hormone produced in the brain that plays a crucial role in social bonding and emotional well-being. Its release is linked to various social interactions, and its impact on happiness is associated with fostering feelings of connection, trust, and overall positive mood. #Happiness Hormones
Endorphins
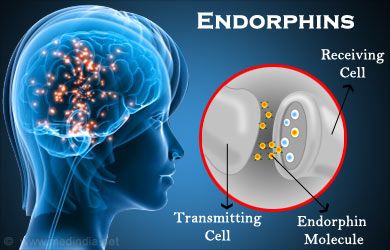
Endorphins image by pinterestEndorphins are natural chemicals produced by the body that act as neurotransmitters, playing a crucial role in the regulation of mood and pain perception. The word “endorphin” is derived from “endogenous morphine,” highlighting its origin within the body and its morphine-like properties. These feel-good molecules are primarily produced by the central nervous system and the pituitary gland, a small gland at the base of the brain. The release of endorphins is triggered by various factors, with physical activity being a major catalyst.
Exercise, particularly aerobic exercise, has been shown to stimulate the production and release of endorphins, leading to what is commonly known as the “runner’s high” — a sense of euphoria and well-being. In addition to exercise, other activities can also prompt endorphin release. Stress and pain are natural triggers; during times of distress or injury, the body often releases endorphins to mitigate discomfort. Laughter is another natural stimulator, as well as activities like listening to music or engaging in enjoyable social interactions. #Happiness Hormones
The impact of endorphins on happiness is profound. When released, these neurotransmitters bind to the brain’s opiate receptors, reducing the perception of pain and creating a positive, blissful sensation. This not only helps in managing pain but also contributes to an overall sense of well-being and happiness. In essence, endorphins act as the body’s built-in mood elevators, providing a natural and effective means of combating stress and promoting a positive mental state. So, next time you’re feeling a bit low, consider lacing up those sneakers or engaging in activities that bring joy — your body’s endorphin boost might be just what you need to brighten your day.
Conclusion #Happiness Hormones
In conclusion, it’s crucial to recognize the significance of happiness hormones in maintaining our well-being. By adopting straightforward lifestyle adjustments, you have the power to elevate these hormones and enhance your mood. Always keep in mind that happiness is a continual journey rather than a final endpoint. Embrace the inevitable highs and lows, and by prioritizing activities that bring you joy, you can ultimately elevate your overall happiness and well-being. #Happiness Hormones
Content Source:
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Dopamine
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serotonin
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxytocin
https://pixels.com/featured/beta-endorphin-molecule-laguna-design.html





Your posts always provide me with a new perspective and encourage me to look at things differently Thank you for broadening my horizons
Your posts always provide me with a new perspective and encourage me to look at things differently Thank you for broadening my horizons
Your posts always provide me with a new perspective and encourage me to look at things differently Thank you for broadening my horizons
Your posts always provide me with a new perspective and encourage me to look at things differently Thank you for broadening my horizons
Thank you for broadening my horizons with your posts, which always give me a new perspective and push me to look at things in a different way.